Configuration for VSCode to code with Python
To write code faster and cleaner we are going to configure Visual Studio Code (VSCode) to auto format the code when saving each file.
Python creates __pycache__ folders and .pyc files in our code, to avoid having cache information displayed in the VSCode’s file explorer we are going to configure it to ignore them.
Linting our code allow us to detect and fix errors, so we are going to install and configure pre-commit to automatically lint our code before every commit.
Make sure you are using a virtual environment
If doesn’t matter if you are creating a FastAPI api, a Flask application or a simple script to automatize some boring task, you should always work on a virtual environment.
Having a virtual environment allows your system’s python to be cleaner (without unnecessary libs installed) and it’s easier for you to test your project with different python versions.
Let’s create a folder for our project and generate a virtual environment inside of it:
mkdir vscode-configuration
cd vscode-configuration
python3 -m venv .venv
NOTE: I’m going to make a tutorial to install python on windows and debian. If you are running ubuntu and this command is giving you errors, you can install python3-venv and python3-dev:
sudo apt install python3-venv python3-dev
Configure virtual environment in your VSCode
You can open the vscode on your current folder typing: code .
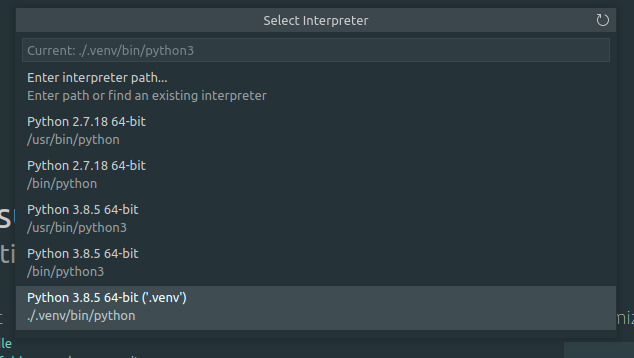
On VSCode press F1 and type: Python:select Interpreter, select your virtualenv or type the route, in our case is: .venv/bin/python/
Format the code after saving a file
To configure our current project we need to create a settings file, so let’s create the .vscode/settings.json file.
To format the code we need to instruct the editor what formatting provider we want to use, in my case i’m using yapf. We need to install yapf to be able to use it, pip install yapf.
The settings.json file allow us to set args for our provider, this is an optional parameter but I prefer to use longer lines than the formatter defaults.
{
"python.formatting.provider": "yapf",
"editor.formatOnSave": true,
"python.formatting.yapfArgs": [
"--style={ based_on_style: pep8, column_limit: 120 }"
],
}
Ignore pycache and *.pyc on file explorer
To avoid displaying this files on the VSCode we just need to add an option in our .vscode/setting.json file:
{
... ,
"files.exclude": {
"**/*.pyc": {"when": "$(basename).py"},
"**/__pycache__": true
},
}
This exclude the folder that are named __pycache__ and also every file ending in .pyc if a file with the same name but with the extension .py exists in the same folder.
Pre-commit settings
In our root folder we are going to create a file to configure our pre-commit tool (./.pre-commit-config.yaml)
This is my configuration but you can set any hook here:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
rev: v2.4.0
hooks:
- id: trailing-whitespace
- id: end-of-file-fixer
- id: check-yaml
- id: check-added-large-files
- id: requirements-txt-fixer
- id: double-quote-string-fixer
- repo: https://gitlab.com/pycqa/flake8
rev: 3.8.0
hooks:
- id: flake8
additional_dependencies: [flake8-typing-imports==1.6.0]
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/mirrors-yapf
rev: v0.30.0
hooks:
- id: yapf
- repo: https://github.com/asottile/pyupgrade
rev: v2.4.1
hooks:
- id: pyupgrade
args: [--py36-plus]
- repo: https://github.com/asottile/reorder_python_imports
rev: v2.3.0
hooks:
- id: reorder-python-imports
args: [--py3-plus]
- repo: https://github.com/asottile/add-trailing-comma
rev: v2.0.1
hooks:
- id: add-trailing-comma
args: [--py36-plus]
We are going to create a ./setup.cfg file with some configurations that are going to be used by the hooks, this is usualy my configuration file:
[autopep8]
max_line_length = 120
[flake8]
max_line_length = 120
[yapf]
column_limit = 120
based_on_style = pep8
To use pre-commit we first need to install it. So let’s run pip install pre-commit.
Now that we have pre-commit installed, we need to install the hooks on our project, we can do this running pre-commit install.
NOTE: pre-commit runs on every commit, so we need to make sure that our folder is a git repository. If you cloned your project from a service, like github, the pre-commit install command will run with no problems. But if you are following this guide we need to run git init in our root folder before running the pre-commit install command.
Pre-commit basic usage:
Assuming you want to commit the changes in all your files you can run the following commands to lint the code.
git add.
git commit -m "test commit"
This will run all the hooks on your modified files and attempt to fix what it can automatically. If the linter doesn’t need user intervention you can add the files that we automatically modified to your commit and recreate the commit.
git add.
git commit -m "test commit"
If any hook is still giving you errors, it’s because they need manual intervention. For example if you are importing a file in the middle of your file, you need to manually move it to the top of the file. After making the changes, run the git add . and git commit -m "test commit" to finally have your commit ready to be pushed after successfully passing your linter.
Pre-commit run on all files:
If you are installing pre-commit in a project that already have code written, you should lint everything so your following commits are cleaner.
pre-commit run --all-files
Pre-commit ignore line
If the linter wants to change a line but you don’t want to, you can specifically set that line to be ignored by the linter.
- Example:
def test(): print( "THIS IS A VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY LONG LINE THAT I SHOULD BUT I DON'T WANT TO MAKE IT SHORTER", ) - The flake8 hook will fail with this message:
flake8.............................................Failed
- hook id: flake8
- exit code: 1
main.py:3:121: E501 line too long (125 > 120 characters)
- With that error we can tell the linter not to check the rule
E501for that line with the comment# NOQA E501at the end of the string:
def test():
print(
"THIS IS A VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY VERY LONG LINE THAT I SHOULD BUT I DON'T WANT TO MAKE IT SHORTER", # NOQA E501
)
- After this change the linter will accept our long line
flake8.............................................Passed
Keyboard Shortcuts
To improve your speed when working with VSCode you can set custom keybindings, I have a post that I’ll continuously update with my custom keybindings, in case you want to try them.